What is a String Wound cartridge filter?
String wound filter cartridge is a type of depth cartridge filter that is made by weaving yarn around a core. Microfibers are twisted and twined together to form a yarn. This yarn is woven in a honeycomb-shaped weave around the core such that it forms a gradient structure to allow better filtration. The quality of a wound filter cartridge hugely depends on the type of yarn that is used to make the filter. The material of the core and a controlled manufacturing mechanism that produces a precise micron rating also contribute. One should bear in mind the filtration application and other involved physical and chemical parameters before choosing a string wound filter cartridge.
The process ensures an effective depth filtration mechanism where the larger particles are caught at the surface, and finer particles are trapped progressively deeper. String wound cartridges are particularly effective due to their versatility and ability to handle high dirt loads.
How does a string wound cartridge filter work?
The string wound filter cartridge is woven to form a gradient density – tighter at the core and lighter on the outside. This means that bigger sediments are filtered out at the onset, and as the liquid passes through the medium, the finer particles get gradually filtered out at every layer. This depth filtration mechanism not only improves the filter’s dirt-holding capacity but also prolongs its operational lifespan. The unique honeycomb weave pattern and precise manufacturing controls ensure that the desired micron rating is achieved.
This design is particularly beneficial in applications where variable sediment loads are present, as the cartridge prevents clogging and allows for continuous filtration without immediate replacements.
Where Are String Wound Filter Cartridges Used?
String wound variants are popularly used for liquid filtration in industries like Food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, water treatment, mining, chemical, oil & gas, gas and air, flue gas, Desalination and automotive.
- Food and Beverage: Ensures purity in production processes by removing unwanted particulates.
- Pharmaceuticals: Provides precise filtration to meet stringent industry standards.
- Water Treatment: Removes sediments, silt, and other contaminants from water.
- Mining: Filters suspended solids and particulates in mining processes.
- Chemical Processing: Handles corrosive chemicals and solvents effectively.
- Oil & Gas: Removes impurities from crude oil and refined petroleum products.
- Gas and Air Filtration: Captures contaminants in industrial air filtration systems.
- Flue Gas Treatment: Reduces particulate emissions in industrial exhaust.
- Desalination: Pre-filters seawater to remove sediments before further processing.
- Automotive: Used in fluid filtration systems to ensure operational efficiency
Best Used For Filtration Of:
- Water
- Alkalis
- Dilute acids and Alkalis
- Organic acids and solvents
- Potable liquids
- Petroleum oils
- Mineral acids
What are the advantages of string wound cartridge filter and why string wound cartridge filter is the best?
The string wound cartridge filter is widely used across industries and for various types of liquid filtration requirements because of its filtration capabilities, high dirt holding capacity, and ability to keep form and last longer. If manufactured to good quality, these types of filters do not collapse under pressure differentials. Additionally, most of the filter housings use ‘knife-edge sealing’ to inset and seal the filter cartridges inside the housing. While other cartridges may be susceptible to poor edge sealing resulting in by-pass problems, good quality string wound cartridges hold their shape and are sturdy.
String wound cartridge filters are favored for their exceptional performance and reliability across numerous applications. Key advantages include:
- High Dirt Holding Capacity: The gradient density design allows these filters to capture more contaminants compared to conventional filters, reducing the frequency of replacements.
- Durability: High-quality materials ensure the cartridges retain their structural integrity even under challenging conditions and high-pressure differentials.
- Knife-Edge Sealing: Most filter housings use this sealing method, ensuring no bypass occurs, a common issue in poorly designed filters.
- Long Service Life: With proper manufacturing and material selection, string wound filters exhibit excellent longevity, making them cost-effective in the long run.
The ability to withstand pressure fluctuations and varying fluid chemistries makes string wound filters an ideal choice for critical applications.
What happens When you use run-of-the mill cartridge filter housing?

If you have overlooked the importance of knife-edge sealing while purchasing cartridge filter housings, then you know how regret looks like! Sometimes overlooking the minutest detail can lead to huge problems. Product Quality Matters.
Poorly designed run-of-the-mill products have no arrangement for inside sealing. This leads to the seepage of water from the infiltration area. In some cases, the rubber gaskets degrade over time. And sometimes the disk sealing the cartridge filter moves from its place, leaving huge gaps for contaminants to seep in. The fitment of the cartridge inside the housing is not right and the product quality is compromised. While making a purchase it is a common tendency to be lured by the extremely cheap pricing, and overlook the minute quality details. What is a filtration system that allows contaminants to pass through? – it is not doing the work it is designed to do. So, if you have ever settled for a poor-quality product for its price, you know well not to repeat the mistake.
Consequences of Using Subpar Cartridge Filter Housings
Overlooking the importance of cartridge filter housing quality can lead to:
- Water Seepage: Poorly sealed filters allow contaminants to bypass the filtration medium, negating the entire purpose.
- Gasket Degradation: Inferior materials degrade quickly, causing leakage and reduced filtration efficiency.
- Displacement Issues: Inadequate sealing mechanisms allow the filter cartridge to shift, creating gaps and reducing performance.
- Frequent Failures: Substandard materials compromise the filter’s durability, leading to frequent replacements and increased operational costs
Investing in high-quality housings with reliable sealing mechanisms ensures consistent filtration performance.
How to select a string wound cartridge filter?
There are four components in a string wound cartridge filter
- Core Material: Choose from polypropylene, gas-filled polypropylene, stainless steel, or tinned steel based on compatibility with the fluid being filtered.
- Yarn Type: Options include natural cotton, bleached cotton, glass fiber, polypropylene, nylon, rayon, and polyester. Each type offers unique benefits, such as chemical resistance or high-temperature stability.
- End Cap: Ensure it is durable and compatible with the housing.
- Gasket: A high-quality gasket prevents bypass and ensures a reliable seal.
A perfect filter is the one that uses appropriate materials and is woven to perfection to fulfil the filtration application requirements. A sturdy core, a premium quality yarn, and high precision manufacturing are some desirable qualities to look for in a cartridge filter. Good quality materials used in the manufacturing of the wound filter cartridge, give it higher filtration capabilities and longer life.
Buy from a string wound filter cartridge manufacturer who has excellent manufacturing capabilities and access to the latest technology. Go local. If you need filtration equipment for a unit based in India, look for a manufacturer who will provide string wound cartridge filter at best price in India. Additionally, a local string wound filter cartridge manufacturer in India will be able to provide faster delivery, and after-sales support will be easy.
Features to look for in a good quality string wound cartridge:
- Chemical free
- Graded density winding
- Precise micron rating
- Minimum media migration
- High dirt holding capacity
- Long service life
- Structural stability
Not using a good quality wound cartridge filter? Here’s what can happen…
• Tunneling
If the yarn used to manufacture a string wound filter cartridge is rounded and smooth, it can easily shift and roll. This displacement/rolling of yarn can happen during ‘knife-edge sealing’ or due to pressure and flow fluctuations. This dismantles the honeycomb structure and creates gaps between the yarn weave and compromises the filtration efficiency. In this case, achieving a precise micron rating is a challenge.
• Chemical leaching
Chemical leaching is a serious concern as it compromises the quality of the filtrate. Often chemicals, resin binders, lubricants, antistatic, and release agents start leaching out as soon as the filter is put to use. they mix with the filtrate and reduce the efficiency of the filtration process. The solution is a) prewash the filter cartridge, and b) let the liquid flow through for some time before using the filter.
However, to ensure minimum leaching it is the best to use filters that are 100% free of resin binders, lubricants, antistatic, and release agents.
• Media Migration
Quality of yarn is one of the important factors that account for the quality of a wound cartridge filter. Short chopped fibers tend to loosen and migrate into the filtration liquid. Rough handling, bad packaging, wear and tear during knife-edge sealing, and inconsistent flows may further cause quality deterioration.
A Complete Guide to Selection of a String Wound Filter Cartridge
What are the various types of cores for a string wound cartridge?
- Polypropylene
- Gas-filled polypropylene
- Stainless steel
- Tinned steel
What are the different yarn types used in a string wound cartridge filter?
- Natural cotton
- Bleached cotton
- Glass fiber
- Polypropylene
- Nylon, Rayon
- Polyester and other
Common Issues with Poor-Quality String Wound Filters
The performance of string wound filters can be severely impacted by poor manufacturing practices and substandard materials. These issues compromise filtration efficiency and reduce the filter’s overall reliability.
- Tunneling: Tunneling occurs when the yarn used in the filter is too smooth, inadequately wound, or improperly tensioned during manufacturing. Under operational pressure, this yarn can shift, roll, or displace, disrupting the honeycomb structure of the filter. This creates gaps in the filtration medium, allowing unfiltered particles to bypass the system. Proper winding tension, a carefully controlled winding pattern, and the use of textured or appropriately processed yarn can mitigate tunneling.
- Chemical Leaching: Substandard filters often incorporate resin binders, lubricants, or other processing chemicals in the yarn. These substances may leach into the filtrate, contaminating the liquid and compromising filtration purity. This is particularly critical in sensitive applications such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, or potable water filtration. To prevent chemical leaching, high-quality filters should be manufactured using chemical-free yarns and undergo prewashing or conditioning to remove any residual contaminants before use. Opting for filters made from FDA-approved or chemically inert materials ensures superior performance.
- Media Migration: Media migration refers to the shedding or release of loose fibers from the filter yarn into the filtrate. This often results from poor-quality yarn, short-chopped fibers, or weak bonding during production. Such migration not only contaminates the filtered liquid but also affects downstream processes. Media migration can be prevented by selecting filters made with continuous-filament yarns and ensuring robust manufacturing practices, including proper fiber bonding and packaging.
- Reventive Measures: Addressing these issues requires a strict focus on quality control, adherence to precise manufacturing standards, and selecting materials that meet application-specific demands. Filters produced with graded density winding, durable core materials, and carefully controlled yarn properties ensure reliability and long-term performance.
What is a Micron Rating?
Micron rating indicates the ability of the filter to remove contaminants by the size of particles. The quality of the yarn and the manufacturing quality have a significant impact on achieving a perfect micron rating. A filter with a 10-micron rating can capture and filter out contaminants as small as 10 microns.
- 50 Microns: Captures particles the size of human hair.
- 40 Microns: Removes particles invisible to the naked eye.
- 25 Microns: Filters out contaminants comparable in size to white blood cells.
- 8 Microns: Captures particles as small as red blood cells.
- 2 Microns: Effectively removes bacteria-sized particulates.
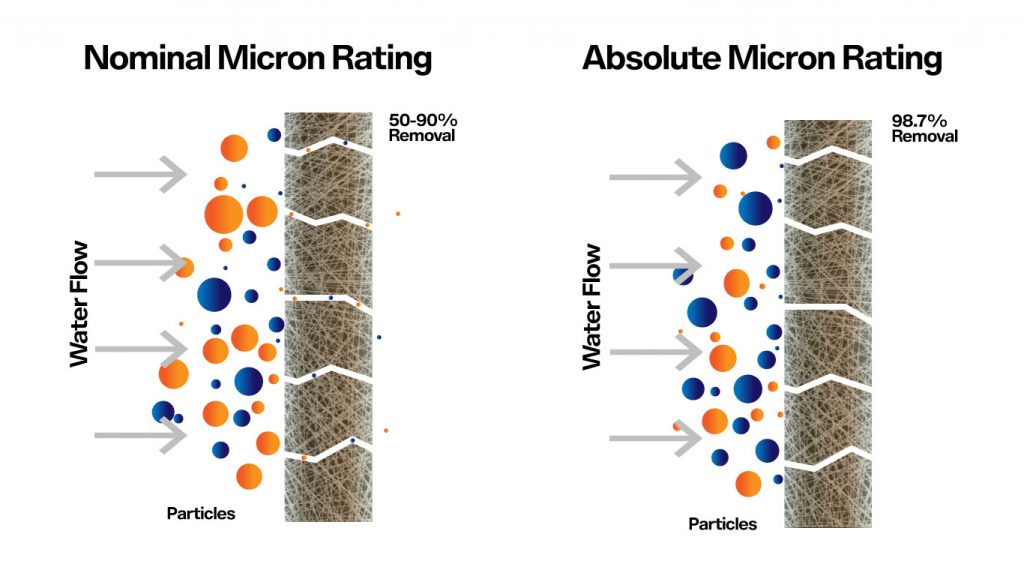
Nominal Micron Rating: Nominal micron rating means that the filter has the ability to capture 50% to 90% of the contaminants of the specified micron size. For example, if the filter has a nominal rating of 50% at 25 microns, it will capture 50% of all the contaminants of size 25 micron.
Absolute Micron Rating: absolute micron rating signifies absolute filtration. Filters with an absolute micron rating are capable of removing 98. 7% or more than 98.7%contaminants of specific microns.
Our Resources
- What is Filter Cartridge?
- What is Melt Blown Filter Cartridge?
- What is a Pleated Cartridge Filter?
- Filtration and Separation
- Why Advanced Pre-filtration for Desalination?
- Advanced Filtration Solutions For Oil And Gas Industry
- Advanced Filtration Solutions For Chemicals & Solvents
- Advanced Filtration Solutions For Pharmaceuticals
- Process and Utilities Water Treatment
Additional Guidance on Selection
Selecting the right string wound filter cartridge is critical to achieving optimal filtration performance. Here are some essential considerations:
- Winding Pattern:The winding pattern should create a gradient density structure, where the outer layers are looser to trap larger particles, and the inner layers are tighter to capture finer contaminants. This design maximizes dirt-holding capacity and extends the filter’s lifespan.
- Yarn Material Compatibility:Select a yarn material that aligns with the chemical, temperature, and physical conditions of the application. For example:
- Polypropylene yarns for general-purpose filtration and chemical resistance.
- Glass fiber for high-temperature applications.
- Cotton for potable water or food-grade filtration.
- Core Material:The core must provide structural integrity and resist environmental stresses. Stainless steel cores are ideal for high-pressure or high-temperature conditions, while polypropylene cores suit standard applications due to their chemical compatibility and corrosion resistance.
Manufacturing Quality: High-quality manufacturing processes minimize common issues like tunneling and media migration. Consistency in yarn tension, precise micron control, and robust bonding methods ensure reliable performance.
Investing in High-Quality Filters: Filters manufactured by reputable suppliers using advanced technologies, such as controlled environment winding systems, ensure superior filtration performance and longer service life. These filters reduce downtime, maintenance costs, and operational disruptions, making them a cost-effective choice for critical applications.
Why Choose Gopani for String Wound Cartridge Filters?
Gopani provides high-quality string wound filters designed for clean and efficient filtration. Our filters remove dirt, rust, and particulates from liquids, making them perfect for water treatment, chemicals, food, pharma, and electroplating. Available in various micron ratings and materials, they offer long service life, high dirt-holding capacity, and strong cores for durability. Every filter goes through strict quality checks to ensure consistent performance. With fast delivery and expert support, Gopani is your trusted filtration partner.
Choose from an exclusive range of String wound cartridge filter variants from Gopani: