How Many Microns Should Your Water Filter Be??
Micron ratings indicate the size of particles the filter can remove from the water, and selecting the correct micron size can ensure that your water is both clean and safe to drink. But with so many options available, it can be confusing to know what micron rating is ideal for your needs. In this blog, we’ll explore what micron sizes mean, how they affect water filtration, and help you determine the best filter for your water quality. Whether you’re looking to remove sediment, chlorine, or bacteria, understanding micron ratings is key to getting the most out of your filtration system.
What is Water Filtration?
The process of removing the particulate matters like suspended particles, parasites, bacteria, algae, fungi and any other unwanted contaminants, biological or chemical contaminants from contaminated water to produce clean and safe water for any purposes such as drinking or pharmaceutical applications.
Importance of Water Filtration in Removing Contaminants:
Removing contaminants from water is important for various applications, especially in industries like pharmaceuticals where purity is paramount. In such cases, even the smallest suspended particles must be eliminated to ensure the production of clean, uncontaminated solutions. Effective water filtration is also essential for maintaining the efficiency and longevity of water treatment systems. Contaminants, if left unchecked, can severely damage sensitive components like RO (reverse osmosis) membranes, leading to costly repairs and downtime. Proper filtration not only protects equipment but also ensures the quality and safety of the water used across different sectors.
How Many Microns Should Your Filter Be?
Factors to consider
Choosing the right micron size for your filter depends on factors like the source of your water, the level of contamination, and your desired water purity. For example, drinking water requires finer filtration than general-purpose water use, while industrial applications may need specific filtration levels to protect equipment or ensure product quality.
Factors to Consider:
- Water Source: Is the water coming from a well, a municipal supply, or a natural source like a river? Well water may have more sediment, while city water may contain smaller particles.
- Contamination Level: Higher levels of contamination will require a smaller micron rating to effectively remove fine particles.
- Desired Water Purity: For drinking water, you’ll need a finer filter to remove bacteria, while irrigation water may not require such precision.
General Guidelines for Choosing a Micron Rating:
- Drinking Water: Usually 1 to 5 microns to remove harmful bacteria and contaminants.
- Industrial Filtration: Can vary widely, but generally uses filters between 5 and 50 microns, depending on the application.
- Sediment Removal: For basic sediment filtration, 25 to 50 microns is typical.
What is a Micron Filter?
Definition of a Micron Filter
Micron Filters are type of filters used to remove dirt, debris and microscopic particles from water or any other fluids by passing them through cartridges with a pore size measured in microns. Smaller the micron rating, the finer the particles that are removed.
How micron filters operate?
Micron filters are important in removing contaminants from water by trapping particles based on their size. These filters are designed with a porous structure, where the “micron” rating refers to the size of the particles the filter can capture. For example, a 5-micron filter will trap particles that are 5 microns or larger, ensuring that smaller contaminants pass through while larger ones are removed. Micron filters are commonly used as a pre-filtration step in industries like pharmaceuticals, where removing larger suspended particles is critical to maintaining water purity. In addition, they protect more delicate filtration systems, such as reverse osmosis membranes, by preventing clogging and reducing the overall load on the system. This not only ensures smoother operations but also extends the lifespan of more expensive, intricate components.
Role of Pore Sizes in Filtering Particles
The pore size of a filter decides its effectiveness in removing particles from water. Filters with smaller pore sizes are capable of trapping finer contaminants, larger pore sizes are better suited for removing larger particles. In applications such as water treatment and pharmaceuticals, selecting the correct pore size is essential to ensure the desired level of filtration. The smaller the pore size, the more thorough the filtration process, but it also increases resistance to flow, meaning the system may require more pressure to maintain efficiency. Finding the right balance between pore size, particle retention, and operational efficiency is key to effective filtration.
Materials used in micron filters
There are several materials used for making a micron filter, the choice of materials are based on purpose the filters are used, for example :-
- Polypropylene (PP): Used for water filtration but limitation with PP filters are that they can not be used in the process where fluides with acidic nature are used or the temperature is high.
- Stainless Steel: This material is highly durable, corrosion-resistant, and reusable, making it ideal for demanding industrial environments, especially those involving high temperatures or harsh chemicals.
- Fiberglass: Effective in capturing fine particles, fiberglass is frequently used in HVAC systems and air filtration due to its high filtration efficiency and low resistance to airflow.
- Activated Carbon: Commonly used for adsorption, activated carbon filters remove odors, gases, and organic compounds, making them essential in both air and water purification processes.
- Nylon: Known for its strength and chemical resistance, nylon is often used in liquid filtration, particularly in the pharmaceutical and food processing industries, where fine particle filtration is crucial.
How Small is a Micron?
Definition of a micron as a measurement.
Micrometer (µm), is a unit of length used to measure extremely small distances. It is equivalent to one-millionth of a meter, or 1µm = 0.000001meters.
Conversion:
- 1 Micron (µm) = 1/1,000,000 meters.
- 1 Micron = 1,000 nanometers (nm).
- 1 Micron = 0.001 millimeters (mm).
Types of Micron Filters
Overview of Different Micron Filter Designs and their Purposes:
Pleated Filters
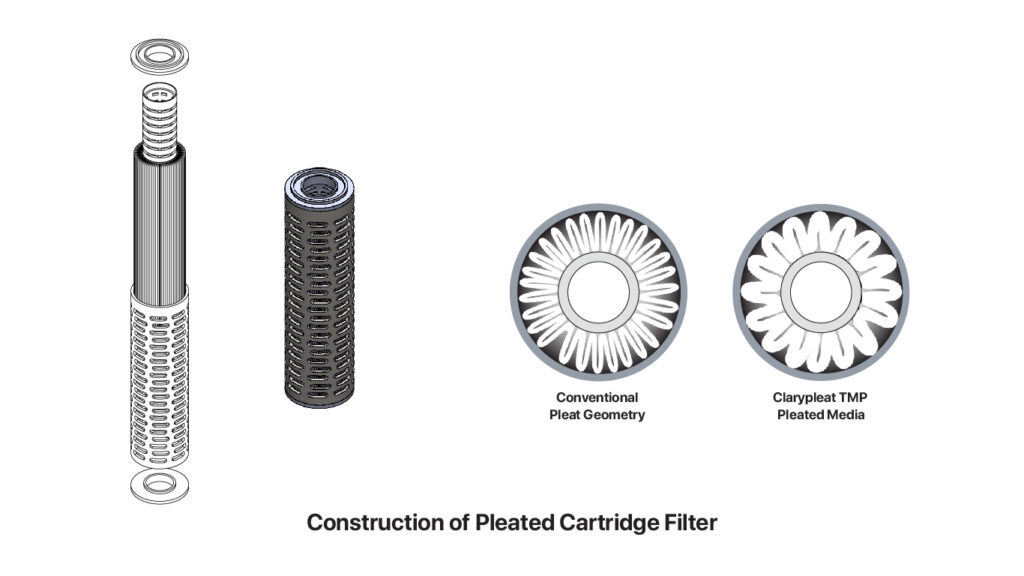
Pleated cartridge filters are surface filters that prevent sediments from passing though the surface. The cartridge media is pleated, so that the surface area of the filter increases and holds a large amount of sediments. The pleated media is engineered to form layers that enable absolute filtration while also allowing it to capture particles of different sizes. Therefore – It aids fine filtration in both nominal and absolute filtration efficiency.
Advantages
- Broad chemical and thermal compatibility
- Larger surface area for higher contaminant holding capacity
Applications
- Deionized water
- RO pre-filtration
- Fine chemicals
- Plating chemicals
- Biological fluids
- Pharma applications
- Ophthalmic liquids
Melt-Blown Filters
Melt blown cartridge filters operate on the principle of depth filtration. The filter media is composed of fine polypropylene fibers that are randomly intertwined. As the fluid passes through the filter, contaminants are trapped within the depth of the filter media. The matrix has a gradient density structure, with smaller pores on the outer surface for efficient removal of larger particles and larger pores towards the core for capturing smaller particles. Melt blown cartridge filters are commonly used as pre-filters in various water treatment processes, including reverse osmosis, desalination, and wastewater treatment. They are effective in removing suspended solids and protecting downstream equipment, such as pumps, membranes, and valves, from clogging or damage.The material used in melt blown filters, exhibits excellent chemical compatibility. It is resistant to a wide range of chemicals, acids, and bases, making it suitable for diverse filtration applications.
Advantages
- 100% free from resin binders, lubricants, antistatic and release agents
- Minimum contaminant unloading and maximum contaminant removal
Applications
- Water
- Wastewater
- Photographic fluids
- Chemicals
- Cosmetics
- Plating solutions
- Inks and Paints
- Weak acids and bases
String-Wound Filters
String-wound filters are made using PP or Cotton strings knitted closely. The yarn is spun over the core in a honeycomb weave on CNC controlled programmable machines that produce precise micron rating. The winding gets tighter towards the core to offer gradient depth for better filtration.
Advantages
- Low pressure drops & high flow capacity
- High dirt holding capacity & low media migration
- Woven to offer a gradient depth for superior filtration
- Long service life
Applications
- Dilute acids and Alkalis
- Organic acids and solvents
- Potable liquids
- Petroleum oils
- Mineral acids
Bag Filters
Filter Bags are used to reduce the load of contaminants downstream.
Sintered Metal Filters
Sintered metal filters are filtration devices that remove particulates from liquids and gases. They are made by compacting metal powder into a mold and heating it to a high temperature, a process called sintering.
- Chemical processing – mostly common in nuclear manufacturing, given that it possesses some of the best properties, including high temperature and corrosion resistance.
- Food and beverage – it is majorly used for the extraction of vital nutrients and juices in food processing. They do not react to food or beverage, thus making them ideal for this application.
- Power generation – Sintered metal filters help in ensuring efficiency and effectiveness in power generation by allowing filtration of water in turbines.
- Petroleum Refining – Sintered metal filters enable you to filter different fuels effectively depending on the degree levels which you require.
- Gas production – this element is suitable for gas production since they don’t react with gases and you can as well use them in different environments.
Different Micron Sizes and Their Uses
Overview of common micron sizes:
- 50 – micron filters: Ideal for large sediment, dirt, and debris.
- 25 – micron filters: General-purpose filtration, suitable for basic water systems.
- 10 – micron filters: Removes finer particles and some bacteria.
- 5 – micron filters: Used in most household water filtration systems for comprehensive sediment and particle removal.
- 1 – micron filters: Fine filtration, capable of removing small particles and most bacteria.
- 0.5 – micron filters: Designed for ultra-fine filtration, removing some viruses and bacteria.
- 0.2 – micron filters: High-efficiency filters used for sterilization, ideal for lab and medical purposes.
Importance of accurate measurement for ensuring filter performance
Ensuring that a filter meets its micron rating is essential for proper filtration performance. Accurate micron ratings prevent particles from slipping through and ensure optimal water purity.
Nominal vs Absolute Micron Filters
Nominal micron filters:
These filters capture a certain percentage (usually around 85%) of particles at the stated micron size. They are ideal for applications where capturing a large portion of particles is sufficient but don’t need total filtration precision.
Absolute micron filters:
These filters capture 100% of particles at the rated micron size, ensuring no particles of that size or larger pass through. These are used when complete filtration is necessary, such as in medical or pharmaceutical applications.
When to use each type based on application needs:
For general water filtration (such as in homes), nominal filters are usually sufficient. Absolute filters are recommended for more sensitive environments like laboratories, healthcare, or when you require precise filtration.
Type of Contaminants Water Filters with Different Micron Ratings Remove
Each micron size removes different contaminants. Here’s a breakdown:
- Micron Rating – Contaminants Removed
- 50 microns – Large particles like sand, debris, and dirt
- 25 microns – General sediment and visible contaminants
- 10 microns – Fine particles, some bacteria
- 5 microns – Most suspended solids, finer sediments
- 1 micron – Bacteria, small particles
- 0.5 microns – Ultra-fine particles, some viruses
- 0.2 microns – Bacteria, cysts, and viruses
How Does Pressure Drop Influence a Micron Filter?
What is pressure drop?
Pressure drop refers to the loss of pressure as water passes through a filter. It happens because the filter material resists the flow of water, causing a decrease in pressure on the downstream side. Pressure drop is an important factor in determining how well your filter performs over time.
How it affects water flow and filtration efficiency?
A higher pressure drop means water flows more slowly through the filter, which can reduce the overall filtration efficiency. When pressure drops too much, the system may struggle to maintain adequate flow rates, resulting in reduced water pressure, slower processing times, or even system failure. Filters with smaller micron ratings tend to cause greater pressure drops since they trap smaller particles, which increases resistance to water flow.
The impact of micron size on pressure drop:
Choosing a filter with a smaller micron size means it will capture finer particles, but it also increases resistance and pressure drop. If the filter is too fine, it may lead to a significant reduction in system performance, forcing pumps or equipment to work harder to maintain flow.
How to Choose the Filter with Proper Micron Ratings?
Assessing Your Water Quality Needs
Understanding what you want to remove from your water is crucial. The type and size of contaminants (sediment, bacteria, etc.) will determine which micron size is appropriate.
Water Source
- Municipal Water: Generally cleaner, so a 5 to 10-micron filter is sufficient.
- Well Water: May contain more sediments or particulates, so a 5-micron filter or larger may be necessary.
- Industrial Use: Filters for industrial water systems depend on the specific contaminants being filtered, ranging from 1 to 50 microns depending on the application.
Desired Level of Purity
For applications that need high water purity (like drinking water or pharmaceutical processes), a smaller micron filter (1-5 microns) is needed to capture finer particles like bacteria and other contaminants.
Equipment Sensitivity and Maintenance Requirements
Highly sensitive equipment may require finer filtration to avoid damage. However, filters that are too fine may clog quickly, increasing maintenance needs. It’s essential to balance the filtration level with operational efficiency.
Advantages of Using a High-Quality Water Filter
Longer Filter Life
High-quality filters are more durable and efficient, meaning they last longer before requiring replacement.
Improved Filtration Efficiency
They capture contaminants more effectively, reducing the amount of particles that can pass through, which ensures better water quality.
Cost-Effectiveness Over Time
Although high-quality filters may cost more initially, they reduce the need for frequent replacements and lower equipment maintenance costs, saving money in the long run.
Reduced Equipment Maintenance and Downtime
Efficient filtration reduces wear and tear on water systems and machinery, minimizing the need for repairs and the likelihood of unexpected downtime.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Are Micron Filters Reusable?
Yes, some micron filters are reusable, depending on the material and design.
Types of Reusable Filters
Typically, stainless steel and some synthetic filters are designed for reuse. They can be cleaned and reinstalled multiple times, extending their lifespan.
Cleaning and Maintenance Procedures
To maintain their efficiency, reusable filters should be cleaned regularly. Depending on the type, they can be rinsed, soaked, or backwashed to remove trapped contaminants.
When to Replace a Filter or Clean It
Even reusable filters have a lifespan. If you notice reduced flow rates, increased pressure drop, or physical damage, it’s time to replace the filter. Over time, repeated cleaning can degrade filter materials, leading to reduced effectiveness.
Why Choose Gopani?
Trusted Expertise:
With decades of experience in filtration, We offer high-quality micron filters that meet the needs of various industries, from pharmaceuticals to water purification.
Precision and Quality Assurance:
We ensure that all our filters undergo a rigorous 7-level quality check process, ensuring that micron ratings are accurate and consistent. This level of precision guarantees reliable filtration performance.
Innovative Solutions:
We provide cutting-edge filtration technologies, including Sintered filters and custom solutions tailored for your needs.
Customer centric Approach:
We work closely with customers to understand their specific needs, providing personalized support and guidance to help them choose the right filtration solutions.
Sustainability and Durability:
Designed for long-term use, our filters reduce the frequency of replacements, promoting sustainability. Our Sintered metal filter options further support eco-friendly practices.
Choosing Gopani means choosing reliability, efficiency, and superior filtration solutions.
Conclusion
Selecting the right micron size is crucial for achieving optimal filtration performance. It ensures that your water is clean and free from unwanted contaminants, while also preserving the efficiency of your filtration system. By carefully assessing your water quality needs, desired purity levels, and equipment sensitivity, you can make an informed decision that balances performance and longevity.
FAQ
What is the best micron level for a water filter?
The best micron level depends on your specific filtration needs. For drinking water, 1-5 microns is ideal, while larger particles in industrial settings might require 10-50 micron filters.
Which is better, a 5 or 10-micron filter?
A 5-micron filter removes smaller particles than a 10-micron filter, making it better for finer filtration, but it may reduce water flow more significantly.
Which is better, 5-micron or 20-micron for well water?
For well water with larger sediment, a 20-micron filter may suffice. However, if finer contaminants like bacteria are present, a 5-micron filter is more appropriate.
Gopani Product Systems
Putting Innovation in Filtration Since 1993
Who we are?
- ISO 9001:2015 Certified
- Quality Conscious
- Forward Thinking and People Positive
- Engineers and Innovators at Work
Resources
- What is Filter Cartridge?
- What is a String Wound Cartridge Filter?
- What is Melt Blown Filter Cartridge?
- What is a Pleated Cartridge Filter?
- Filtration and Separation
- Why Advanced Pre-filtration for Desalination?
- Advanced Filtration Solutions For Oil And Gas Industry
- Advanced Filtration Solutions For Chemicals & Solvents
- Advanced Filtration Solutions For Pharmaceuticals
- Process and Utilities Water Treatment
Our Trending Cartridge Filters Products
- Melt Blown Cartridge Filters
- String Wound Cartridge Filters
- Pleated Cartridge Filters
- ClaryFlow Big Buddy
- High Flow Filter Cartridges and Housings